Spam webpages have always plagued search engine results pages (SERPs), creating poor user experiences, and it’s been getting worse. A 2024 research study found an increase in low-quality, mass-produced content created purely to game Google search results.
The sleeping giant finally awakened, and Google struck back with its March 2024 core update — targeting unoriginal, low-quality, and AI-generated content.
Following the update, Google added manual penalties to improve the quality of search results further, deindexing hundreds of websites — many of which previously had traffic in the millions.
What does this seismic shift in Google’s algorithm and the search engine optimization (SEO) industry mean for your business? Let’s investigate.
Google’s March 2024 Core Update: A Summary
The 2024 core update changed Google’s core ranking system’s search algorithm and spam policies.
Reducing Unhelpful Content by 40%
The new update builds on its helpful content update from 2022 that introduced an internal ranking signal to gauge a website’s helpfulness to searchers. While Google has released two more helpful content updates since then, the March 2024 core update marks a substantial shift in how Google determines helpful content and identifies high-quality websites.
According to Google’s estimates, the March 2024 update algorithm changes, and prior updates together will reduce unoriginal, low-quality search results by 40%. Key changes in the March 2024 core update include:
- Merging helpful content and core updates: Google merged the helpful content update with its usual core update, signaling an end to the series of stand-alone helpful content updates.
- Moves away from a single ranking signal: Instead of using a single site-wide ranking signal, Google has adopted a mix of innovative signals and approaches to identify helpful content and high-quality websites.
- Considers page and website together: Google now looks for unhelpful and unoriginal content at both page and website levels to prevent off-topic spam from being hidden among other pages.
New Spam Policies Against SEO Abuses
In addition to tweaking the search algorithm, the Google March 2024 spam update also introduced new policies that define the type of content Google considers spam.

The update added the three abuses to Google’s spam policies:
- Scaled content abuse: Google considers pages created purely for search engines and lacking original, valuable content as spam regardless of the creation method (humans, automation, or a mix of both). Previously, Google‘s spam policy only penalized auto-generated content.
- Site reputation abuse: Third-party content published on a website to benefit from its ranking signals without any apparent link between the two is treated as spam. For example, if a movie review website hosts a page about the best casinos, Google flags it as spam.
- Expired domain abuse: Buying an expired domain to show spammy, low-quality content in search is now called expired domain abuse. For example, a website owner posts affiliate product reviews on a recently expired non-profit charity domain.
Google finds these abuses via automated systems and a team of manual reviewers. Manual penalties for a website violating Google spam policies range from a drop in SERPs to complete removal from Google’s index. Website owners are then sent a penalty notice via Google Search Console. That said, if a website is affected by the automated algorithm updates rolled out, the webmaster won’t be notified.
If you’re violating any of these new policies, start removing spam content even if you haven’t received a manual penalty from Google yet. Spam is a ticking time bomb.
The Blogsmith founder, Maddy Osman, ranked among top 100 content marketers by Semrush and BuzzSumo, shares that “While there’s no reputable source we could find confirming any direct relationship between manual and automated algorithm indexing, experience suggests that it’s fair to assume the former influences the latter.”
Manual Penalties From Google: Examples
The March 2024 Google core update continues to roll out in stages, but Google’s renewed fight against spam is already causing big changes in search results. Let’s look at a few examples of the major manual penalties levied so far.
1. ZacJohnson.com
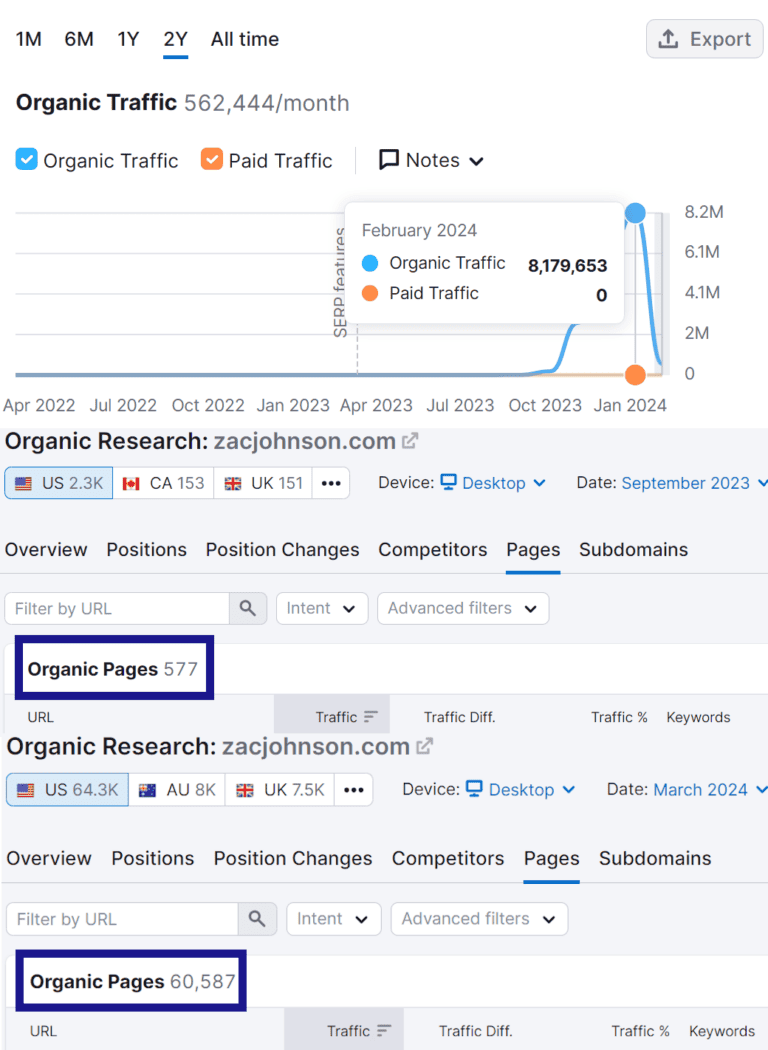
- Traffic before de-indexing: 8,179,653
- Likely spam penalty: Scaled content abuse
ZacJohnson.com published over 60,000 articles from September 2023 to March 2024, averaging more than 325 blog pieces daily.
While massively scaling up its content production, ZacJohnson.com published unrelated topics — celebrity gossip, best-of content, and random trending ideas — to attract traffic. Google’s manual reviewers probably considered this a classic case of a website made for search engines and serving ads instead of providing a good user experience for people.
2. FreshersLive.com
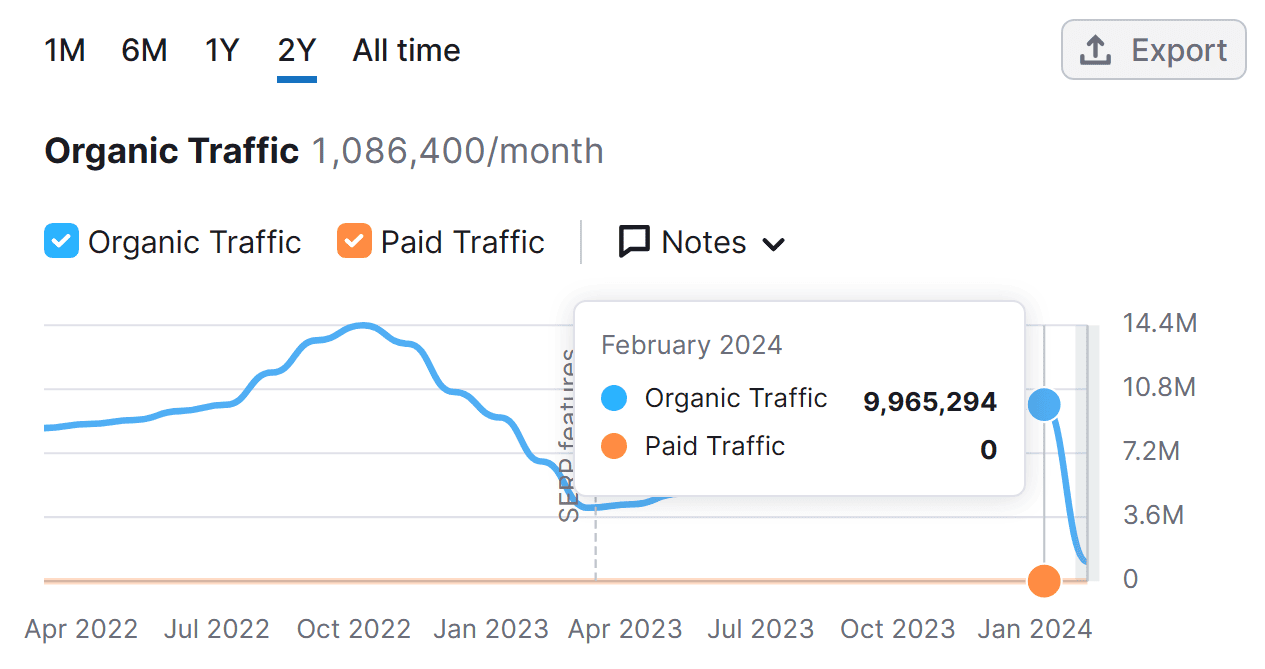
Screenshot
- Traffic before de-indexing: 9,965,254
- Likely spam penalties: Misleading functionality and too many ads per page
Screenshot
FreshersLive most likely caught the attention of manual reviewers due to the number and nature of ads served to visitors on each page. When we visited the website, we encountered a deceptive ad that led to a YouTube channel instead of what it promised — which Google terms misleading functionality.
3. Hooke Audio
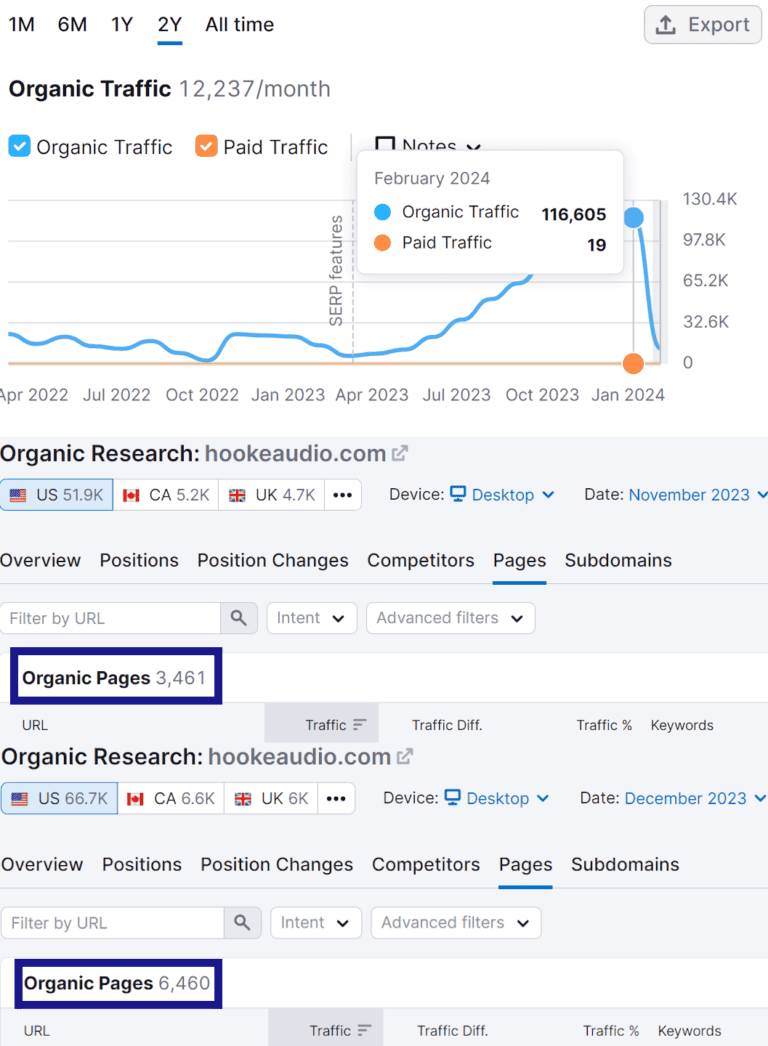
Screenshot
- Traffic before the de-indexing: 116,605
- Likely spam penalties: Scaled content abuse and little or thin content.
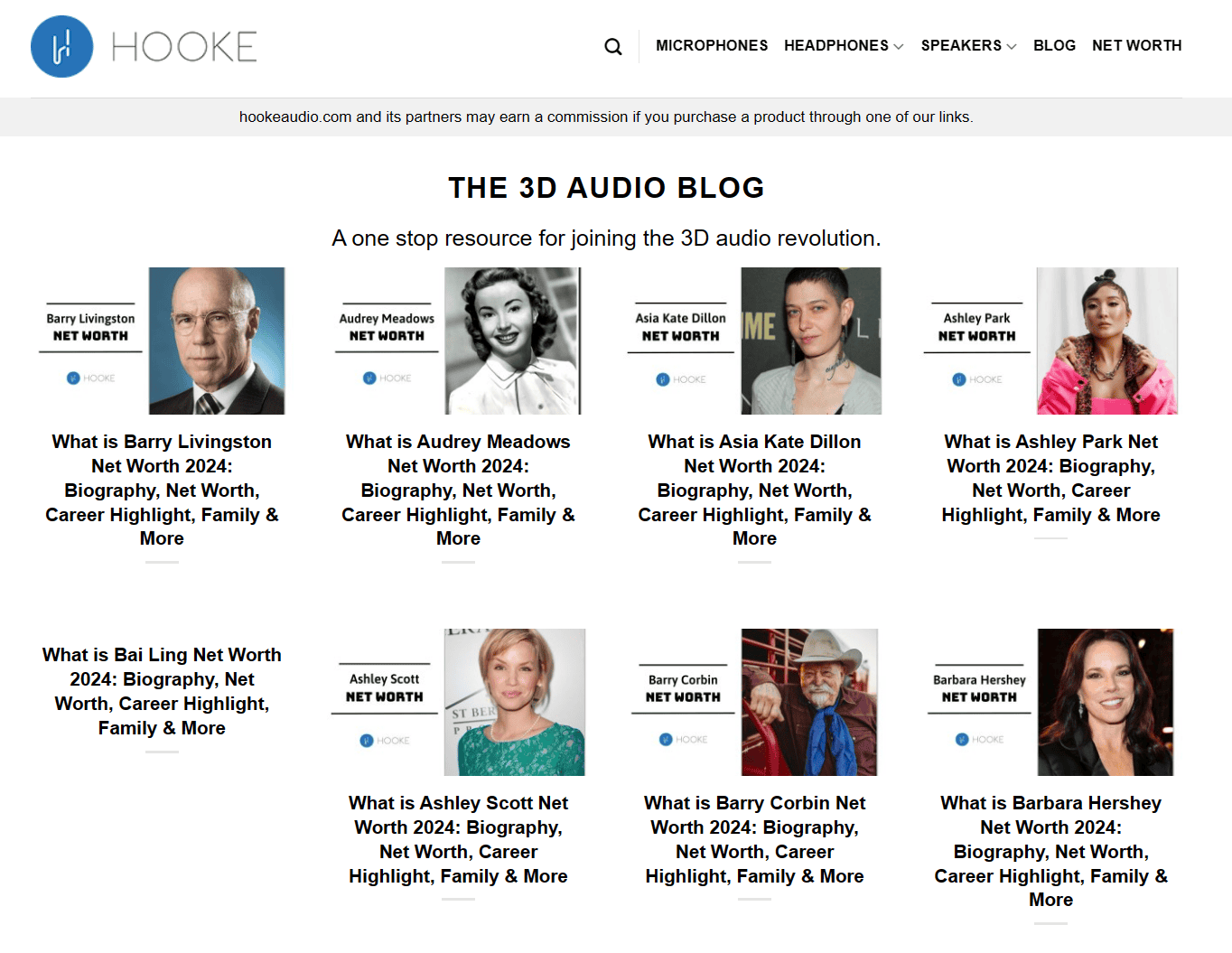
While Hooke Audio claims to be a “one-stop resource for joining the 3D audio revolution,” its webpages appear to cover mostly unrelated topics. In one month, it published 3,000 pages on trending topics that manual reviewers likely considered unhelpful and thin.
Screenshot
Moving Forward: Takeaways From Google’s March Core Update
Given the new Google algorithm changes, updates to spam policies, and manual penalties, content creators must adjust SEO strategies to protect SERPs.
1. Avoid Over-Reliance on AI
Leveraging AI-based tools has many benefits, and Google allows AI-generated text. That said, Google expects you to add value with your content, where an AI might fail if it regurgitates incorrect or widely available information.
In fact, 50% of the websites that received a manual penalty used primarily AI-generated content.
Instead of looking at the number of pieces published as your primary metric, focus on high-quality content and good user experiences. Avoid using AI tools for content creation from start to finish and instead use AI tools to automate time-consuming, menial tasks in keyword research and content ideation.
2. Attune Your Website to Google’s Changing Guidelines
Google’s March core update and prior helpful content changes are just part of the continuing Google algorithm updates. Google continually adjusts to counter bad actors and improve search results. Past pivotal core system updates included:
- Panda (Feb. 2011): Introduced a quality signal that penalized websites with duplicate content, thin content, or keyword stuffing.
- Penguin (April 2012): Penalized websites with unnatural backlinks acquired by purchasing links or using private blog networks.
- Fred (March 2017): Targeted websites practicing aggressive monetization instead of serving website visitors with helpful content.
Google updates are released every few months, and to keep your website on Google’s good side, you must stay in the loop. Check out the Search Quality Rater Guidelines to get a head start on understanding Google’s guidelines.
At The Blogsmith, we’ve always believed in creating helpful content for humans, packed with unique insights instead of adding more noise to search engines. We also frequently update our content style guide to adapt to the changing Google guidelines so our content doesn’t experience major ranking volatility after new algorithm updates.
3. Leverage Experts To Create Value
While generative AI is an easy target, low-value content isn’t unique to AI tools. After all, Google has been battling spam since long before the birth of GPT-based tools.
One way to ensure your content adds value instead of noise to the search engines is to rely on expert voices in your field.

Screenshot
At The Blogsmith, we do thorough research on each topic, prepare a list of questions for subject matter experts, and follow up with insightful queries to create a valuable content piece full of exclusive insights.
4. Focus on Creating a Brand
Manual actions from Google can hit any size website. Before being de-indexed, FreshersLive.com had higher traffic numbers than even TechCrunch.
To establish a long-term presence in search rankings, you need to build your brand, create value, and offer a fulfilling experience to the readers.
Start by working on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trust). Focusing your content creation on people-first content, adding detailed author bios, and interacting with the community helps earn the trust of your readers.
5. Quality Over Quantity
Google continues to prioritize valuable content for its readers, not content volume. So, if you have to choose between quantity and quality of content pieces, always choose quality.
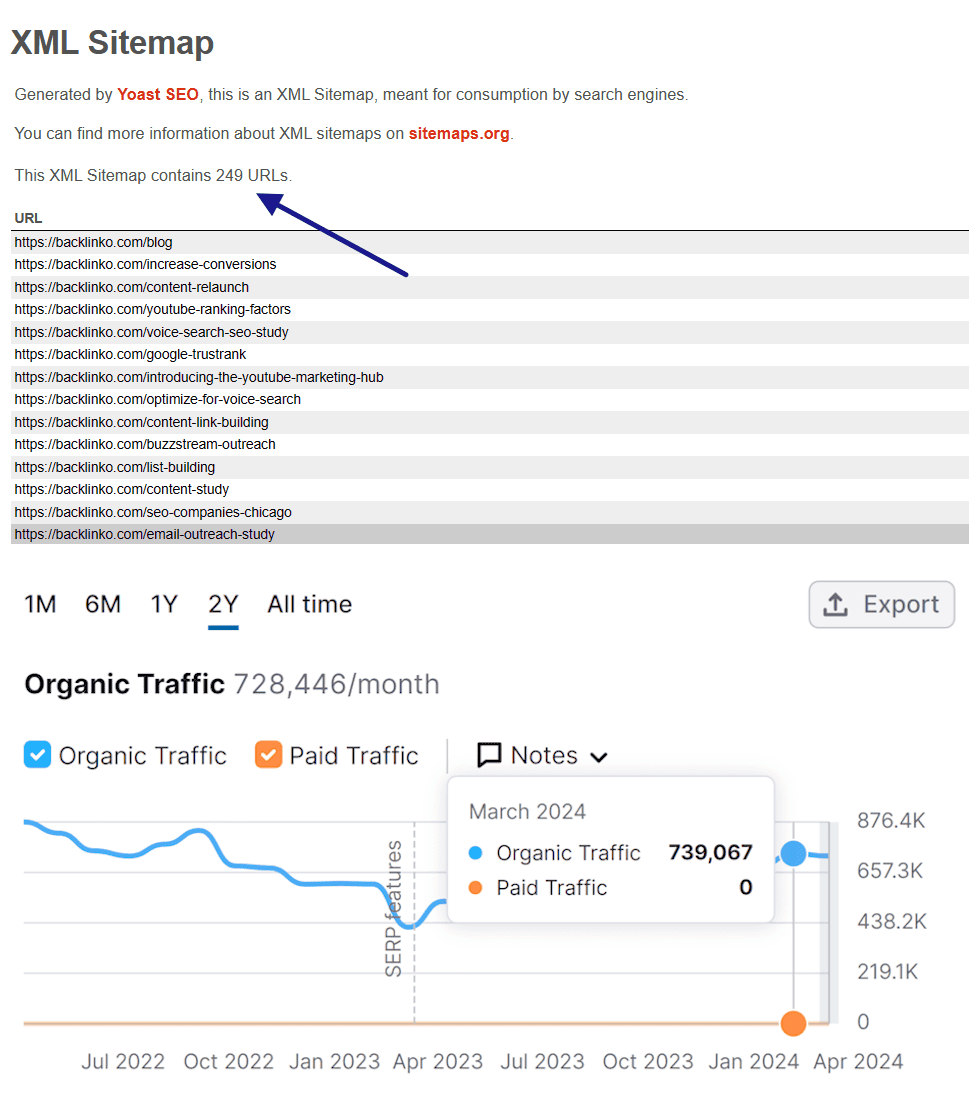
For example, Brian Dean’s Backlinko only has 249 content pieces but enjoys healthy traffic because he’s earned his audience’s trust by creating insightful content pieces.
Final Thoughts: Google’s March 2024 Core Update
If you create spam at scale, you’re creating problems at scale that you’ll eventually have to clean up. Plus, there are no guarantees that Google will return your website to their index after a cleanup. Just do it right from the start, and you can scale results in a maintainable way.
While unethical SEO techniques (black-hat SEO) offer short-term gains, they also come with long-term headaches, so don’t be fooled.
If you’re struggling to scale up your content creation without creating spam, you need an experienced team of experts to help.
Contact The Blogsmith and discover how a full-service content marketing agency can help you build an audience without cutting corners.